On July 30 and 31, GIZ and the Biomass Energy Industry Promotion Association of China (BEIPA) co-organized the virtual Sino-German Biomethane Workshop under the framework of the Sino-German Energy Partnership (EP). The event aimed at presenting and discussing the German experience in terms of policies, incentives, technologies, standards and business models for biomethane production and grid injection, as well as to discuss its implication and applicability for China. During the event, a comprehensive study conducted by the German Institute for Biogas, Waste Management and Energy commissioned by GIZ on the same topic was officially launched.
Why biomethane production?
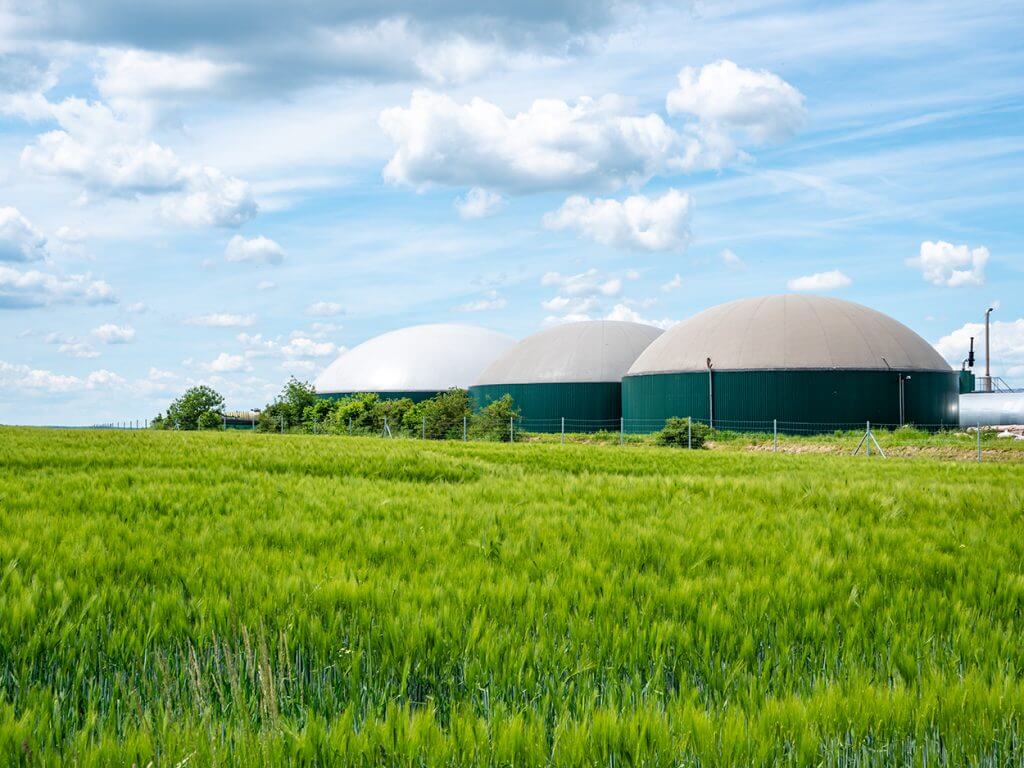
Biomethane, typically upgraded from biogas by removing the CO2 from the gas mixture, is a green, low-carbon, clean and renewable natural gas. Produced from anaerobic fermentation and purification of crop stalks, livestock and poultry manure and other municipal organic waste, it is a zero-carbon energy carrier for power, heating and transportation. The application of biomethane provides an excellent and flexible alternative to conventional natural gas and other fossil energy sources. The biogas and biomethane industries are significant and growing contributors for the global decarbonization and combating climate change. As calculated by the World Biogas Association, the sector has the potential to reduce worldwide GHG emissions by 10-13% (World Biogas Association, 2019).
Although the potential for biomethane development in China is huge, with an estimated capacity of 60 billion cubic meters per year, only 100 million cubic meters/year are currently produced. In addition, China’s biomethane is in the early stage of development, facing an inadequate industrial system, technical and further challenges. In 2019, ten ministries, including the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) and the National Energy Administration (NEA), jointly issued the “Guidance on Promoting the Industrialization of Biomethane Development”. The document proposes that by 2030 China’s annual production of biomethane should target over 20 billion cubic meters. Until then, China should accelerate the development of biomethane and establish a sound biomethane industry system.
German experience – policies, incentives, technologies and business models
Since 1991, Germany has been actively promoting the use of renewable energies for power generation in order to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the energy sector. With more than 200 biogas plants and a total production capacity of up to 130,000 cubic meters per hour, Germany has extensive practical experience in the biomethane sector.
During the event, Prof. Frank Scholwin and Mr. Johan Grope, Institute for Biogas, Waste Management and Energy, gave a comprehensive introduction of biomethane production and grid injection in Germany. Unlike other countries, German support schemes neither include a direct gas-grid feed-in tariff for biomethane nor direct funding of the biomethane production itself. Instead, there are several indirect support schemes or obligations focused on increasing the share of renewable energies (including biomethane) in electricity generation, heating and mobility. The boom in biomethane plants in Germany is primarily due to the Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG), which first supported biogas generation in 2004. In 2009, a revision of the law granted even more generous support for biomethane and triggered strong growth of the biomethane sector. However, the current feed-in tariff (FiT) of around 14 ct/kWhel (a result of an EEG revision in 2014) hasn’t generated much new growth in the sector. Nevertheless, as FiTs are guaranteed for 20 years, electricity production is expected to remain the largest market for biomethane in Germany for the next decade.
Implications for China
The report discusses both German best-practices as well as their implications for China. Suggestions for China, drafted by Chinese experts from the Biomass Energy Industry Promotion Association (BEIPA), include a vision for the development of the biomethane sector in China and policy recommendations, such as the improvement of policies and regulations, the establishment of a biomethane monitoring and regulatory system, industry standards, testing and certification systems.
Click here for the study “Biomethane production and grid injection: German experiences, policies, business models and standards” in English
Click here for the study “Biomethane production and grid injection: German experiences, policies, business models and standards” in Chinese