Climate Goals and Recommendations for Action in China’s Transport Sector

The transport sector is a key sector with regards to fossil fuel consumption, and its energy consumption and GHG emissions have been widely concerning. In recent years, China’s transport sector has made great efforts in promoting energy conservation and emission reduction, and has achieved significant results. However, there are still many problems and challenges existing in the field of transport which need to be managed, in order to accelerate the processes of energy saving and carbon reduction, and promote the realization of carbon dioxide peaking and carbon neutrality.
Developing Smart Logistics for Sustainable Transport

This study focusses on the smart logistics’ influence on sustainable and low carbon development, differences as well as similarities in the understanding and application of smart logistics in China and Germany are presented. Based upon this research, a common understanding of smart logistics is proposed, and an analysis of key driving factors and future development trends of smart logistics applications in China and Germany is provided. Finally, recommendations for the further and effective development and implementation of smart logistics are put forward based on the findings of this study.
Transport and Climate Change Week 2022: Insights & Experience from China Shared at Global Sustainable Transport Conference

The 5th Transport and Climate Change Week (TCCW) took place between 9th and 13th May, 2022. It is an international conference focused on knowledge-sharing and peer-to-peer exchange on the challenges and best practices for achieving sustainability goals and decarbonisation in the transport sector. Around 1,500 experts and decision-makers from around the world joined the week-long conference through its online platform, where they could follow and engage with the events, as well as connect in online networking spaces.
Insights from China: How can we decarbonise the transport sector?

During the global online conference Transport and Climate Change Week 2022, the Sino-German Cooperation on Low Carbon Transport (CLCT) project was pleased to invite Mr Xu Honglei, vice president at the Transport Planning and Research Institute (TPRI) of the Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China, to share insights on the key challenges and ongoing efforts in decarbonising China’s transport sector, and the steps needed to stimulate its green development.
From ‘Mobility-on-demand’ to ‘Mobility-as-a Service’: Promoting China’s Transition Towards Sustainable Transport Integration
The MaaS study first analyzes the definition and global practices of MaaS. Then it depicts the current landscape, stakeholders, and barriers for China’s MoD services. With field investigations in Beijing, the Guangdong-Hongkong-Macau Greater Bay Area, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, and Foshan, local trails of MaaS cases in China were made. Based on the assessment of key components towards MaaS, the study provided policy recommendations for the further integration of MoD and the development of a Chinese MaaS ecosystem to the MoT.
Strategy Workshop for the SUMP Foshan: Finding a path for Foshan’s green mobility transition

As a milestone of the Foshan SUMP pilot implementation, the online workshop was held by CSTC and GIZ with participation of CATS and the Foshan Transport Bureau as well as other local stakeholders and experts. The workshop was aimed at finalising the core elements of the strategy for the SUMP: scenario selection, vision, and objectives. During the workshop, the participants discussed 3 future scenarios (by 2035): 1. Rail-dominated development; 2. Balanced bus & rail development; 3. Multi-modal development. Selecting the 3rd scenario further informed the discussion of the vision and objectives of the SUMP. Finally, 37 city-level measures corresponding with the SUMP vision (incl. integrated transport planning, stronger motor vehicle management, and creating a vibrant active mobility environment), were introduced to gather initial stakeholder feedback.
E-Bus Development in China: From Fleet Electrification to Refined Management
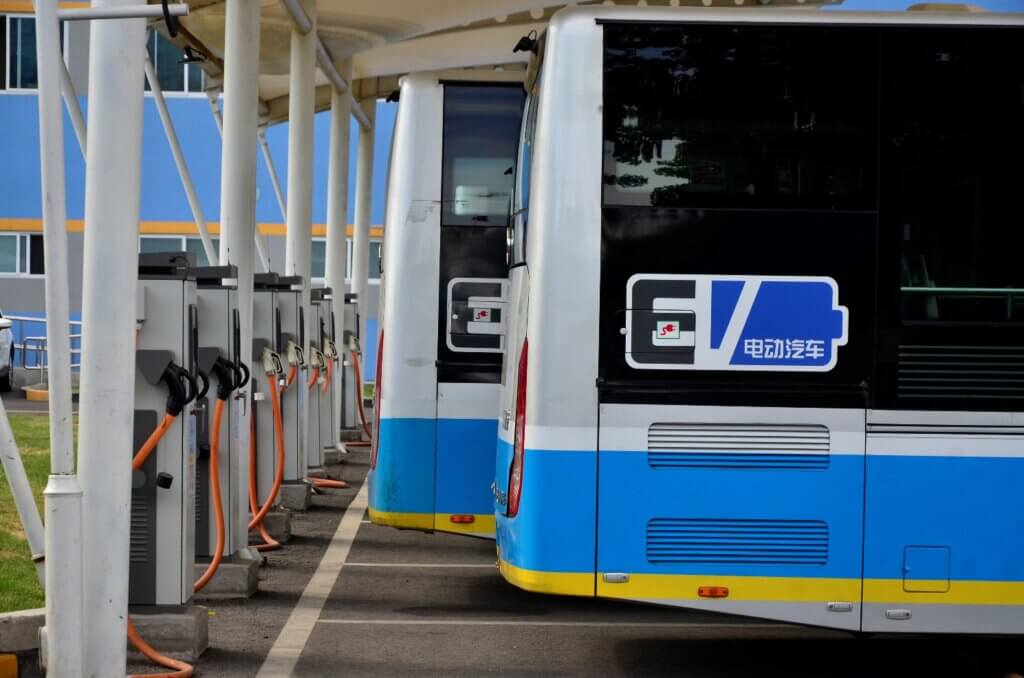

The “Study on Technical System of the Life Cycle of Battery Electric Buses” follows the life cycle stations of battery electric buses, from its procurement, charging, operation, maintenance, to the decommissioning of batteries. It provides a technical guide for stakeholders in each of the procedures to achieve safety, efficiency, and sustainability. As part of the study, eight case cities covering various geographic area and social-economic level were identified: Zhengzhou, Chengdu, Shenzhen, Jinan, Guangzhou, Shenyang, Yinchuan, and Xi’an. Through surveys and interviews, the study collected first-hand data on the challenges, solutions, and best practices in these cities. Based on literature review, comparative analyses, field study, and expert consultations, the study then provides recommendations for all relevant stakeholders.
How will the new German government approach transport?

On December 8, 2021, a new German federal government was inaugurated. The new coalition of three parties consists of the Social Democrats, the Liberals and the Greens. The partners have developed a 177-page coalition agreement to define a programme for government work until 2025, which is focusing on the green and zero carbon transformation of the German economy.
NDC-TIA Workshop: Climate Targets and Impacts in the Transport Sector in China
On October 29 2021, the National Determined Contribution Transport Initiative For Asia (NDC-TIA) project, together with the European Union Chamber of Commerce in China (EUCCC) jointly held the workshop “Climate Targets and Impacts in the Transport Sector in China”. The workshop aimed to facilitate international experience sharing on climate strategies, targets and policy making in the transport sector and to provide a platform for relevant stakeholders to discuss the pathway towards achieving the climate targets in the transport sector, with a focus on four key areas (energy, road freight, aviation and shipping)
China’s updated Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)
On 28 October 2021, three days ahead of the 26th UN Climate Change Conference of Parties (COP26), China submitted its updated Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).