A Sino-German Comparative Study of Urban Logistics and Last-mile Delivery Processes
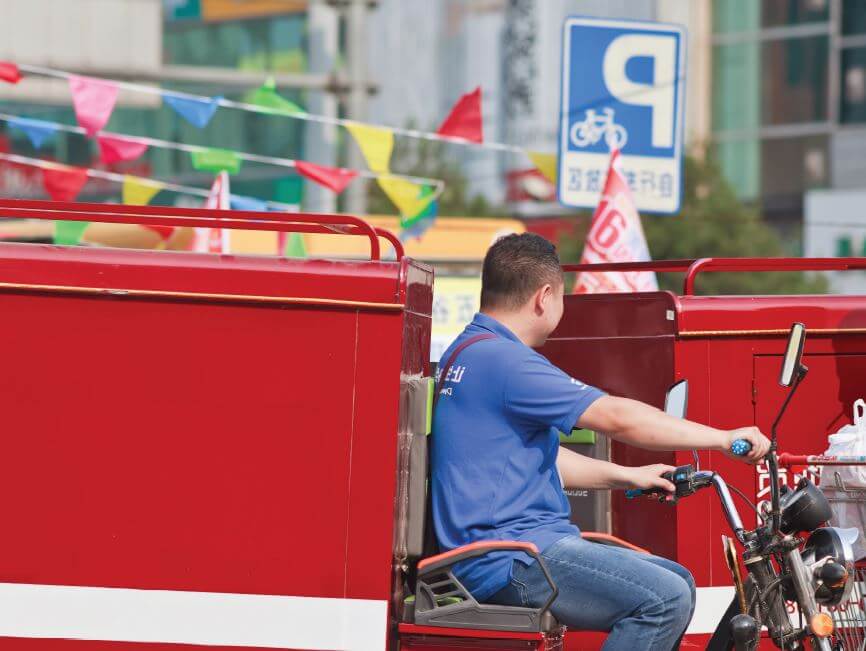

With the modernisation of cities, the need for urban logistics is growing and the parcel delivery market is becoming increasingly important in countries around the world. With its huge volume of express parcels and developed online retail system, China has huge demand, market and potential for parcel delivery. For this reason, the parcel delivery market […]
Status Quo of China’s Drone Industry – Market Development, Regulation and Application

This report helps to better understand the developments in the Chinese drone market and drone industry as well as the legal framework, to trace different approaches to pilot projects and to assess the future potential of this sector.
Electrification of Taxi Fleets in China and Germany – Status Quo and Policy Recommendations
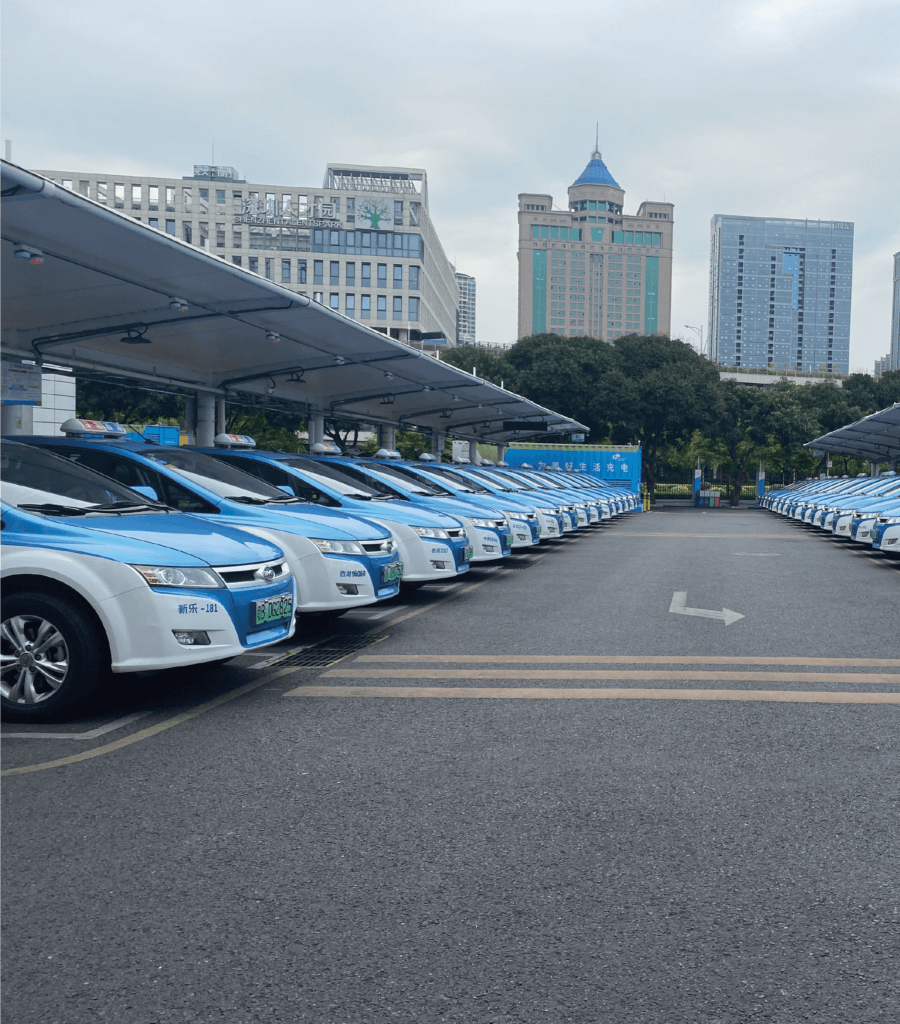

The electrification of large vehicle fleets, especially taxi fleets, is a necessary component for achieving international and national climate targets. This measure can also make an important contribution to reducing particulate matter and noise pollution in cities. In China, local governments are increasingly intervening in the design of urban taxi fleets through regulatory measures by […]
High-Speed Railway Development for a Sustainable Transport Transition

The reduction of domestic and short-distance flights depicts an important tool to decarbonise the transport sector. Considering the rapid expansion of the high-speed rail (HSR) network in China, studies point at a significant diversification of people´s mobility choices, strengthening of intercity relations and overall benefits for the socio-economic development due to HSR development. The present […]
Comparative Study on Urban Logistics and Last Mile Delivery Processes in Germany and China
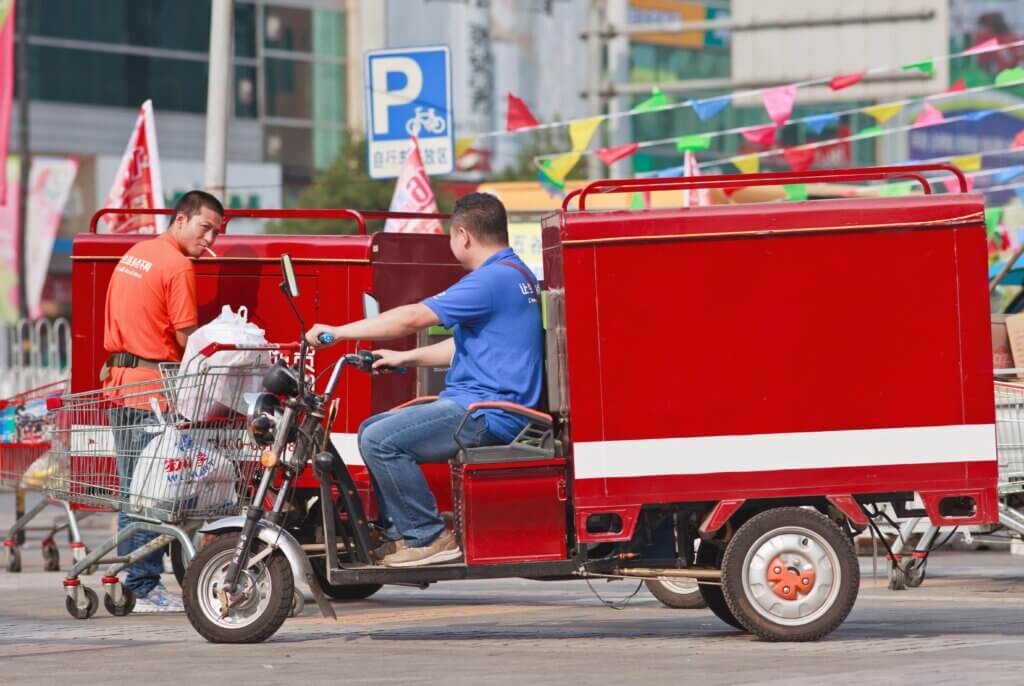

This study by the Bergische Universität Wuppertal (BUW) focusses on the comparison of the last mile delivery organisation and urban logistics in Berlin, Germany and Suzhou, China. It builds on two previous studies about the courier, express and parcels (CEP) markets in Germany and China. Furthermore, the study takes a look at Berlin’s and Suzhou’s city profiles in terms of economy, transport, and parcel delivery network. By comparing the cities’ structures and their approach to last mile deliveries, greenhouse gas emissions saving potentials for Berlin will be analysed and discussed.
LIGHT ELECTRIC VEHICLES FOR A GREEN TRANSPORT TRANSITION: REGULATORY APPROACHES, MANAGERIAL CHALLENGES AND MARKET POTENTIALS IN GERMANY AND CHINA

How can electric micro and light vehicles become drivers of an urban transport transition and unleash their potential, rather than congesting sidewalks and sparking municipal dissent? Individual transit below the category of cars relies on relatively low-cost, agile and oftentimes environmentally friendly vehicles with the potential to reduce inner-city car congestion and improve urban quality of life.
BARRIER-FREE TRANSPORT: OVERVIEW OF DEVELOPMENTS IN THE EUROPEAN UNION AND GERMANY
Barrier-free transport is a key element of sustainable, climate-friendly and inclusive cities. This report gives an overview of the main policies, standards and best practices regarding barrier-free transport in Germany and the EU. It’s part of the work on Sustainable Urban Mobility Planning (SUMP) and the bilateral exchanges between Germany and China on sustainable transport, which is implemented by the sustainable mobility team of GIZ in China.
CASE STUDY RESEARCH ON URBAN LOGISTICS AND LAST MILE DELIVERY PROCESSES IN GERMANY
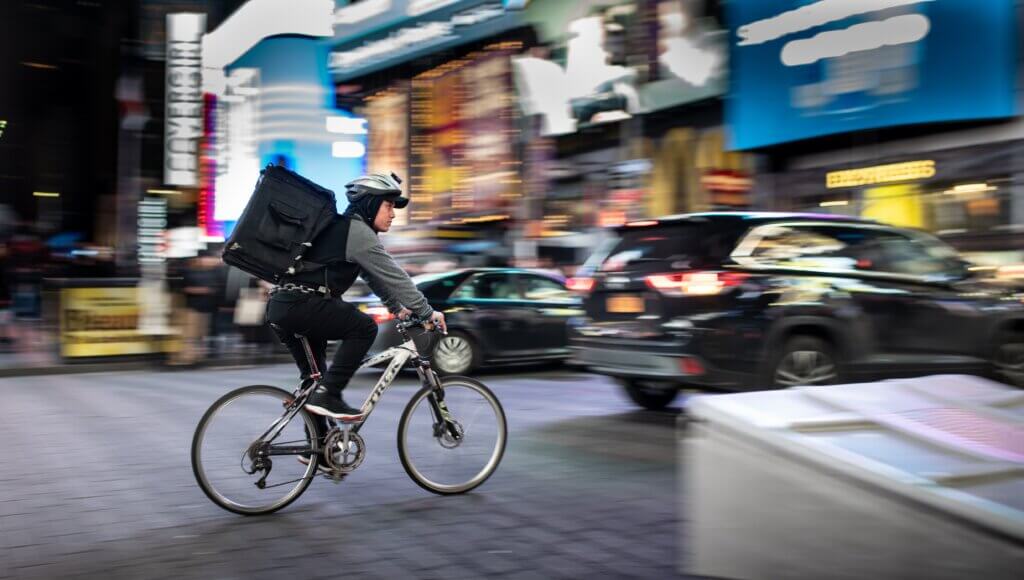

The growth of e-commerce has changed distribution in cities worldwide. E-commerce is heavily dependent on a reliable and short delivery time to fulfil the main interest of the end consumer: Immediate availability and rapid delivery of goods. To meet such consumer demands, while reducing the environmental impacts and increase cost efficiency of courier, express and […]
Sustainable Strategies for Ports

As part of the study, research was conducted on best practices in green logistics in the international ports of Rotterdam (Netherlands), Los Angeles (USA), Singapore (Singapore), Hamburg (Germany) and Risavika (Norway). Simultaneously to this analysis, a survey was conducted in the Chinese ports of Ningbo-Zhoushan, Tangshan and Tianjin. The aim of the comparison was to identify potential for improvement and optimisation in Chinese ports.
Analysis and assessment of energy efficiency in automated container terminals – Example of Tianjin Port
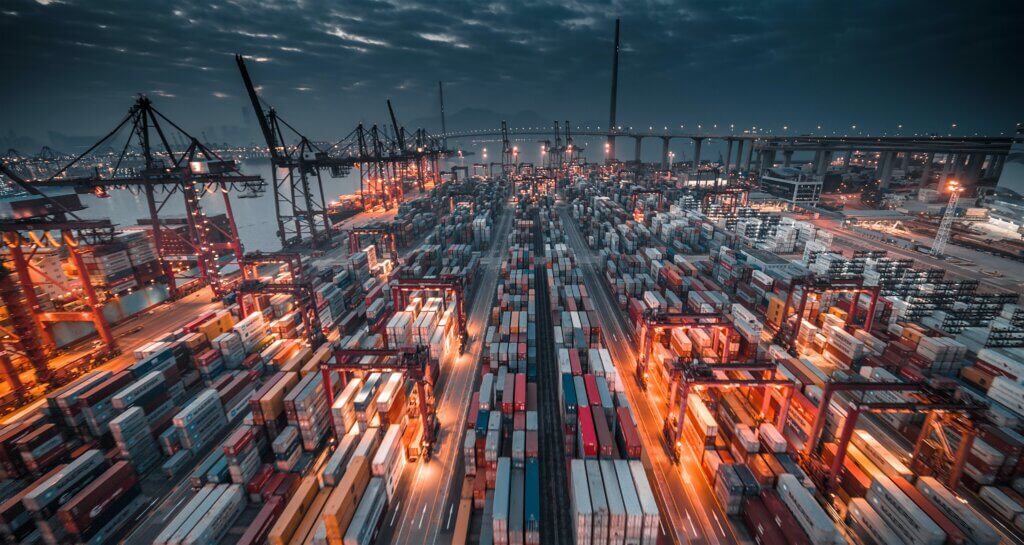

Automation of container terminals and port processes promises a sustainable way to save energy, which is essential for a sustainable development of logistics. The aim of this study was to evaluate this ecological optimization potentials of the port of Tianjin by modernizing the terminal equipment and automating terminal processes. Investigation site is the “Five Continents […]