On 12th October, 2021, as part of the ITS World Congress in Hamburg, the Sino-German Cooperation on Low Carbon Transport (CLCT) project of the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH organised the session Mobility-as-a-Service: International best practices on low carbon transport and mobility integration. The session brought together Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) operators and experts from Europe, India, and China to present on MaaS development in different regional contexts.
The speakers included Mr Sampo Hietanen of MaaS Global and its MaaS platform Whim, Mr Michael Bartnik and Ms Johanna Hofmann of the Berlin-based MaaS platform Jelbi, operated by the Berlin Transport Authorities (Berliner Verkehrsbetriebe, BVG), Mr Tim-Sören Hohmann of the GIZ India project SMART-SUT, and Mr Gregor Bauer of the Sino-German Cooperation on Low-Carbon Transport (CLCT). The session was moderated by Ms Julia Nagel of CLCT.

The ITS World Congress is an annual event dedicated to promoting intelligent transport systems through a diverse technical programme and an international trade exhibition. This year’s ITS was organised by ERTICO (ITS Europe) and hosted by the city of Hamburg between 11th and 15th October. Over these five days, over 13,000 attendees from countries worldwide visited the exhibitions and presentations all around topics of smart mobility and the digitalisation of transport. The congress aims to showcase what the future of transportation and mobility may look like, this year under the motto “Experience Future Mobility Now.”
With the exhibition part to a large degree focused more on car-based travel, particularly with regard to autonomous driving and related technologies, the technical programme of the Congress sought to further explore mobility concepts aimed at reducing the demand for and prevalence of cars in the urban landscape, such as Sustainable Urban Mobility Planning (SUMP) or Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS). MaaS is a concept aimed at the integration of public transport and private mobility services into one digital mobility platform, ultimately facilitating an entire urban trip, from route-planning to payment.
The session Mobility-as-a-Service: International best practices on low carbon transport and mobility integration brought together speakers from MaaS Global/Whim and BVG’s Jelbi as some of the foremost practitioners of MaaS in Europe, as well as representatives of GIZ projects on MaaS development in China and India. Each speaker contribution highlighted the findings and potentials of MaaS development in their respective regional contexts, as well as prevailing challenges.
Speaker Contributions
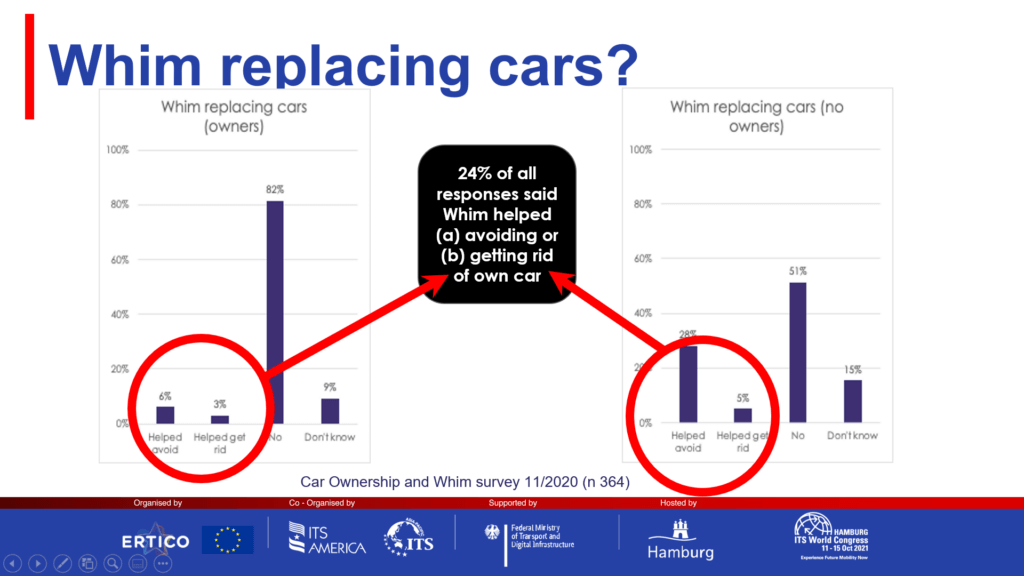
Mr Sampo Hietanen, founder and CEO of MaaS Global, presented on the already visible impacts of the MaaS platform Whim in Helsinki, Finland. Through a 2020 survey of Whim users it was found that the MaaS platform helped 24% of respondents to avoid buying or indeed to give up their own car. Mr Hietanen further discussed the 2019 study by Ramboll entitled ‘Whimpact’ – highlighting several key findings from examining MaaS operation in Helsinki – as well Whim’s recent launch in the Japanese city of Kashiwa.
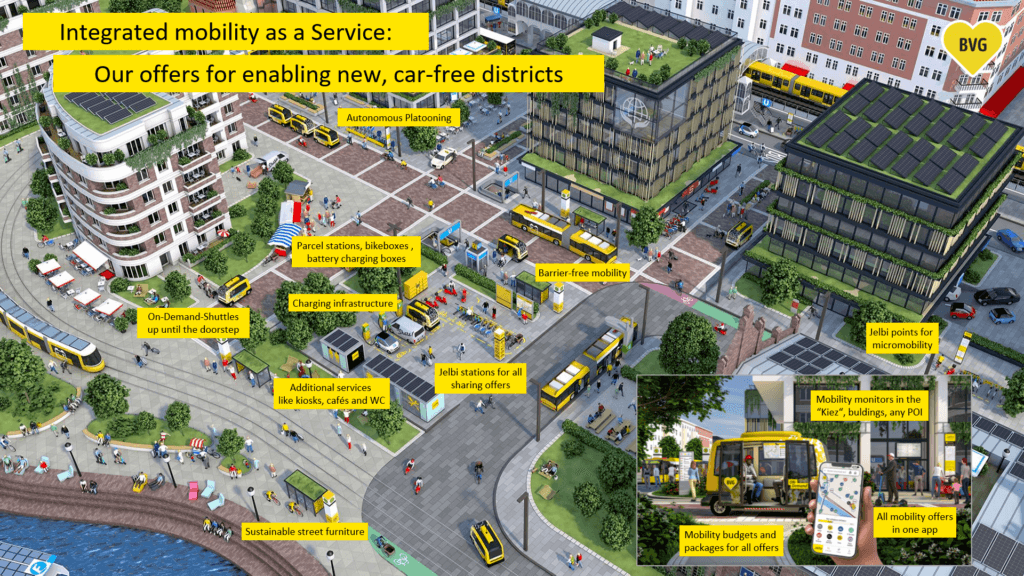
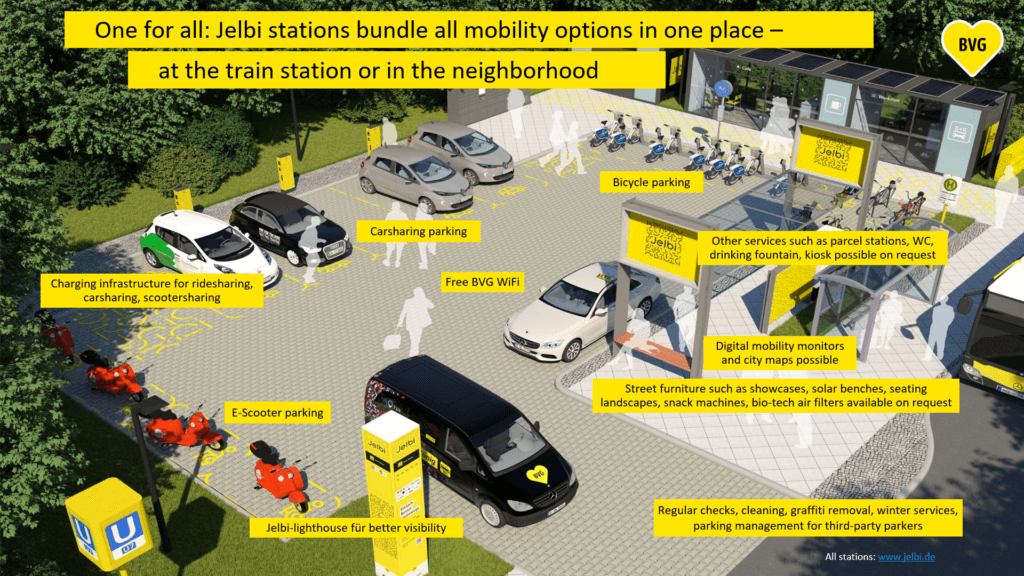
Ms Johanna Hofmann, Project Manager for Jelbi (Stations), and Mr Michael Bartnik, Project Leader Jelbi Digital Transformation and Innovation, presented on how Berlin bundles public and private mobility, as well as on a pilot implementation and further plans for car-free districts and neighbourhoods in the city. The speakers also showcased the establishment of Jelbi stations, which gather multiple Jelbi provided transport modes into one accessible hub located at public transport stations.
Mr Tim-Sören Hohmann, Advisor at GIZ India, outlined how the SMART-SUT project supports their partners in MaaS development. The project has introduced a wide set of recommendations to the Indian partner Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) for developing a comprehensive data policy conducive to MaaS implementation. An online platform for Indian transport professionals and decision makers that analyses a city’s readiness for MaaS development was developed by the project and presented during the session (see Figure below). It will officially be launched at the online Urban Mobility India Conference on 29th October, 2021.
For further information on the MaaS activity of SMART-SUT, please contact Mr Narendra Verma (narendra.verma@giz.de). For requests regarding the overall Indo-German cooperation in sustainable transport, please refer to the head of the project, Mr Jürgen Baumann (juergen.baumann@giz.de).

Mr Gregor Bauer presented a research project on MaaS development in China commissioned by the CLCT project and conducted by the China Urban Sustainable Transport Research Centre (CUSTReC), a research institute of the China Academy of Transportation Sciences (CATS) under the Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China (MoT). After a brief outline of the rapid development of Mobility-on-Demand services (MoD) in China, namely ride-hailing, bike-sharing, and car-sharing, the presentation focused on two city cases of MaaS development.
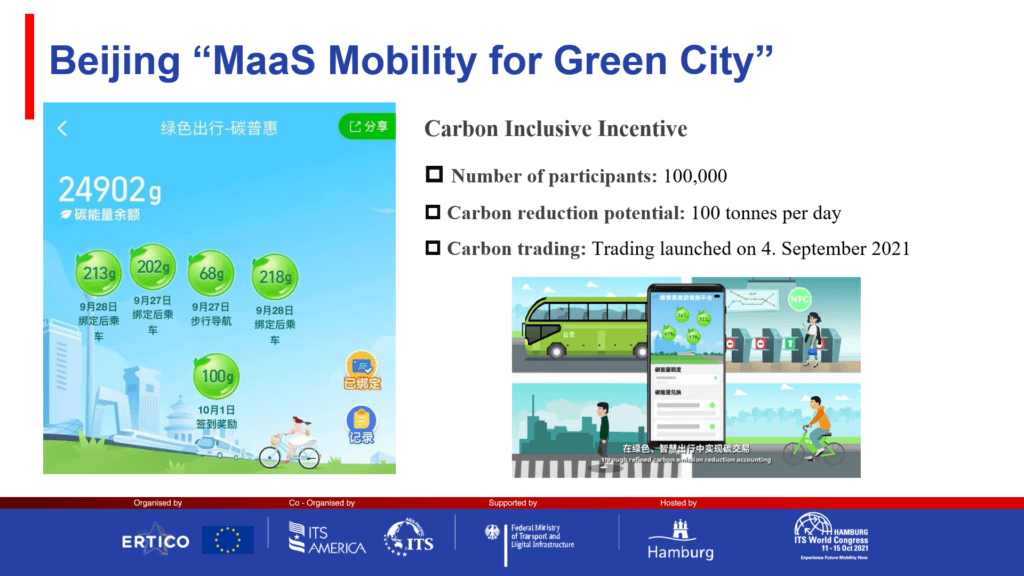
The first case is the “Green Pass” (绿通票) from the city of Guangzhou. As a public-private cooperation between the city’s public transport payment system and the leading ride hailing app Didi Chuxing, “Green Pass” provides a bundled bus and bike-sharing service, with plans to integrate further transport modes. The second case is the “MaaS Mobility for Green City“ initiated by the city of Beijing. Through using the navigation service provided by Amap and Baidu map, users collect credits for their avoided carbon emissions when choosing public transport, cycling, and walking. The collected green credits can then be exchanged for services or coupons, providing a financial incentive for choosing green mobility. The initiative is based on Amap trading the collective green credits of all participating users on the Beijing carbon market. Find out more in our article on the initiative.
The CLCT study on MaaS focuses on the development of MoD services in China and their transition into MaaS as a key to climate-friendly mobility. In benchmarking to international best practices, the study analyses the latest development of MaaS in China and identifies the remaining obstacles for effective integration and low carbon aspects of MaaS development. The study team is currently finalising policy recommendations reflective of the research findings and aims to propose a MaaS framework tailored for the Chinese context.
For more information on the research project, please get in touch with Ms Chenzi Yiyang (transition-china@giz.de), technical advisor of Sino German Cooperation on Low Carbon Transport project.