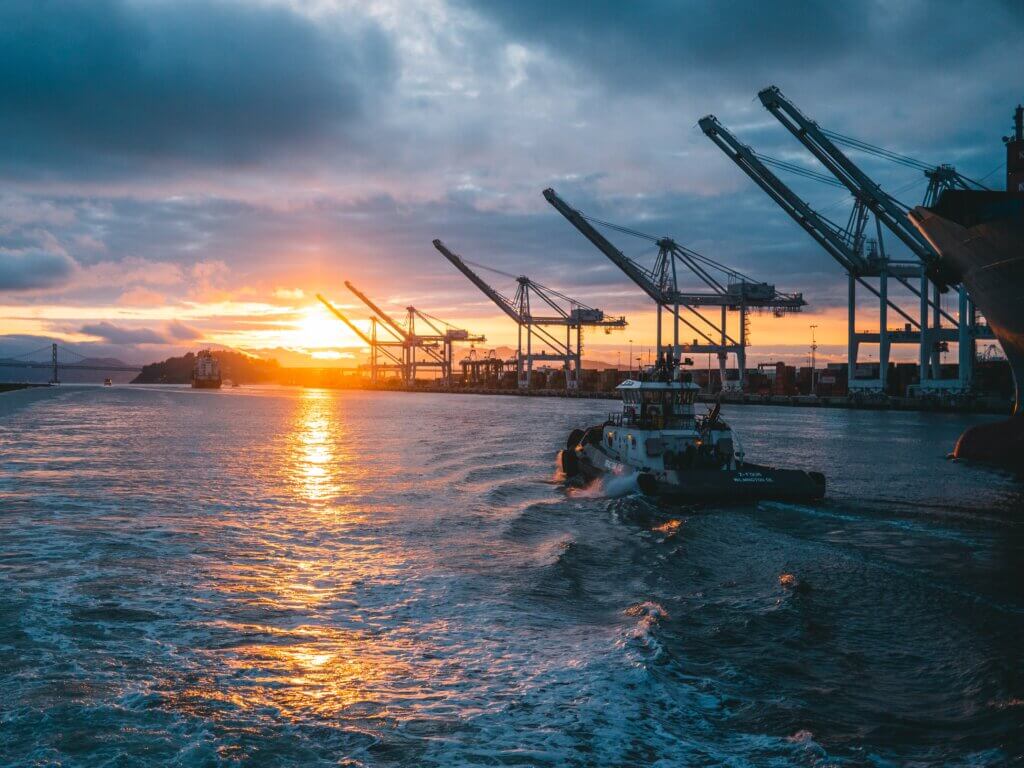
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) assumes that international shipping causes around 2.2 % of global greenhouse gas emissions. Ship emissions also contain sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides and soot particles, which have a negative effect on local air quality and are a major source of pollution in many port cities and coastal waters. By using shore power supply solutions for ships, local emissions can be almost completely avoided, and greenhouse gas emissions can be reduced significantly. The aim of this study is to identify and formulate recommendations for action to promote the comprehensive use of shore power supply for ships in the port of Tianjin.
To introduce this topic, the study starts by discussing the development and spread of technologies for shore power supply and explains the technical requirements for the use of such systems in ports. Building on this, the use of shore power supply systems in selected ports is analyzed and evaluated according to the following aspects: Berths for ships and systems; Organization and institutions for energy supply from land to ship; Costs and incentive mechanisms; Operational experience; Assessment of the port. Based on this analysis, best practices are then identified, which serve for the final derivation of recommendations for action for the port of Tianjin. The following recommendations for action can be derived:
- Introduction of the obligation for all ships calling at the port of Tianjin to use shore power supply (similar to the situation in the USA).
- Allocation of financial resources (subsidies) for the port of Tianjin to cover the comparatively high costs both for the expansion of the supply systems and for their operation.
- Establishing partnerships between the port of Tianjin and shipping companies to promote investments in on-board equipment and to agree on standards and procedures for operation and maintenance.
- Provision of subsidies and other incentive measures (for shipping companies and ship operators) to cover the costs of shore power supply.
- Improvement of operational safety through the development of systems with a high degree of automation.
- Development of management systems and the introduction of training courses for port staff in the operation and maintenance of shore-side equipment.
This short technical study was developed jointly by the Fraunhofer Institute for Systems and Innovation Research (ISI), the Fraunhofer Center for Maritime Logistics and Services (CML) and the port of Tianjin. As part of the study, interviews and literature research were mainly carried out for the comparative analysis of shore power supply systems in the ports of Tianjin (China), Hamburg (Germany), Vancouver (Canada), Gothenburg (Sweden) and Trelleborg (Sweden).
If you would like to know more about shore-to-ship power supply systems, you can download below the full report.
The report is a product of the Sino-German Cooperation on Mobility and Fuels Strategy (MFS) as a Contribution to the Mobility and Transport Transition, which is implemented by GIZ on behalf of the Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure (BMVI).
Responsible for the report is Mr Alexander von Monschaw, GIZ in China.