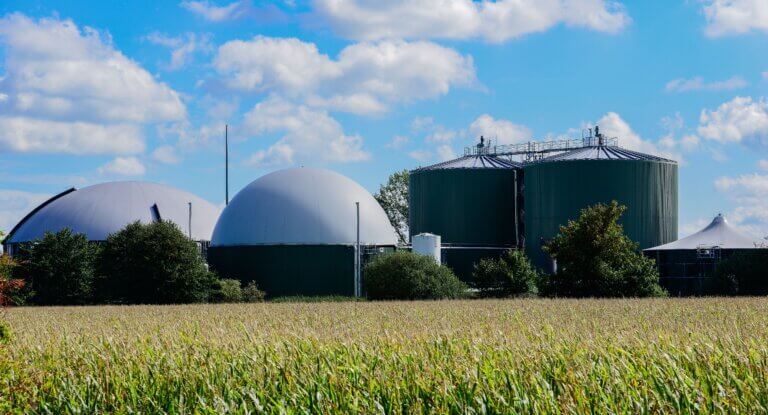
Straw clean-heating is being promoted in Northern China
China has abundant crop straw resources. According to statistics, the annual resource utilization is about 837 million tons, and about 137 million tons are not effectively utilized. In recent years, the Chinese government has attached great importance to the problem of clean-heating in the northern regions and encouraged the promotion of biomass heating technologies such as straw in rural areas to replace traditional raw coal combustion and alleviate air pollution.