International Standards for Sustainable Infrastructure: An overview

Infrastructure investments are inherently long-lasting and, taken as a whole, infrastructure has a profound impact on the economies, environment, and society of the places where they are located. Decisions taken at the planning and investment stage of the infrastructure sector—such as in roads or energy facilities—often have implications that last for generations, and guide settlement […]
Plus Energy Buildings & Districts

Germany’s building sector accounts for about a third of the country’s total greenhouse-gas (GHG) emissions and 40 % of total energy consumption. The continuous enhancement of building standards is a key element to reduce CO2 emissions of buildings especially during the operational phase. In recent years, several models to maximise thermal performance of buildings have been developed. Well-known examples are the Passive House, the nearly Zero Energy Building (nZEB), and the Plus Energy Building as the next ambitious step in the evolvement of highly energy efficient construction.
Energy Efficiency of Buildings & Energy Districts in Urban Renewal

This document is part of ten Keystone Papers looking at current emerging topics in the building and city sector, focusing on energy efficiency and resilience. The Keystone Papers were developed within the framework of the Sino-German Urbanisation Partnership as a basis for its working topics.
ENERGY SAVING DESIGNS IN BEIJING DAXING AIRPORT

Beijing Daxing International Airport officially opened on this Wednesday. Although being one of the biggest airports in the world now with four runways and a 700,000-square-meter terminal area, the airport is walking-friendly — within a walking distance of 600m or 8 minutes, passengers can arrive at the terminal centre from the transport hub. It also offers various new technologies including facial recognition and robotic parking system etc. Besides these, energy and environment is also an important concern.
SPONGE CITY CONSTRUCTION AS A MAJOR ADAPTATION MEASURE IN CHANGDE CITY

With the annual rainfall 1200-1500 mm and the majority falls in spring and summer, the city of Changde faces the severe risk of urban inland flood and its intensity goes even worse when climate scenarios show more fluctuating in precipitation. Meanwhile, with the rapid progress in urbanization and industrialization, urban rivers turned to muddy and smelly with the surface overflowing with cyanobacteria. In the purpose of updating city infrastructure to be as flexible as a sponge in adapting to environmental changes and inland flood risk, as well as addressing the urban river pollution issues, sponge city has been strategized as a key measure to deal with water problem and as a core urban adaptation approach.
POLICY BRIEF: URBAN ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE IN CHINA
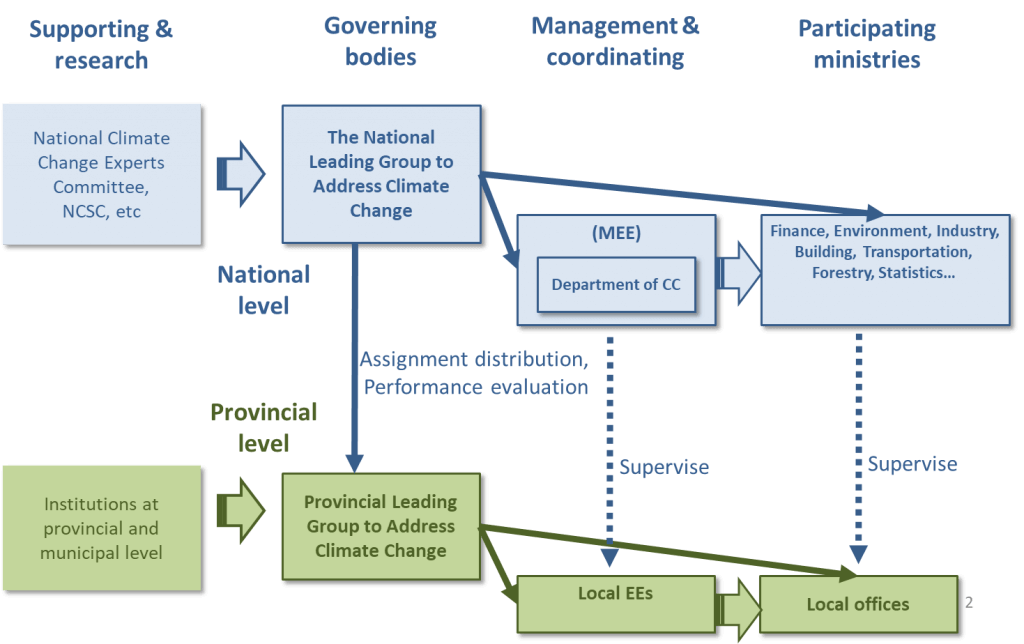
In the Outline of the 12th Five-Year Plan (FYP) for National Economic and Social Development of the People’s Republic of China, issued in 2010, it was the first time that addressing climate change was established as a separate chapter, putting forward the strategic requirements for enhancing capacity for climate change and considering impacts of climate change in planning and urban construction.
ENERGY-EFFICIENT BUILDINGS IN CHINA: STANDARDS AND FINANCING MECHANISM

From the first Chinese Design Standards for Civil Buildings in 1986 to the recent released National Standard of Green Buildings Assessment, policy on energy efficiency and carbon emissions of buildings, including retrofitting old ones and constructing new ones, has undergone significant changes in the past decades in China.
Urban Renewal in Districts
This document is part of ten Keystone Papers looking at current emerging topics in the building and city sector, focusing on energy efficiency and resilience. The Keystone Papers were developed within the framework of the Sino-German Urbanisation Partnership as a basis for its working topics.
Perspectives of stakeholders on sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure Standards

Stakeholder Testimonies on Sustainable and Resilience Infrastructure Standards


